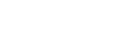Is Crypto Really Anonymous? Uncovering the Truth About Privacy in Blockchain
Is Crypto Really Anonymous? Uncovering the Truth About Privacy in Blockchain
Is Crypto Really Anonymous? Uncovering the Truth About Privacy in Blockchain
Is Crypto Really Anonymous? Uncovering the Truth About Privacy in Blockchain
Shashank Kothari






Due to the misconception that cryptocurrency guarantees total privacy, many users believe they may make transactions without leaving any identity record.
Because blockchain technology is complex and sometimes misinterpreted, the myth that cryptocurrencies provide total anonymity endures. Although specific features offer a degree of privacy, anonymity falls in some aspects.
This post will reveal the truth about blockchain privacy by analyzing the distinctions between anonymity and pseudonymity, how privacy might be jeopardized, the role of privacy coins, crypto traceable transactions, blockchain analytics, and best practices for safeguarding your privacy. We’ll explain what happens behind the scenes of crypto transactions and provide practical ways to enhance privacy.
Anonymity vs Pseudonymity
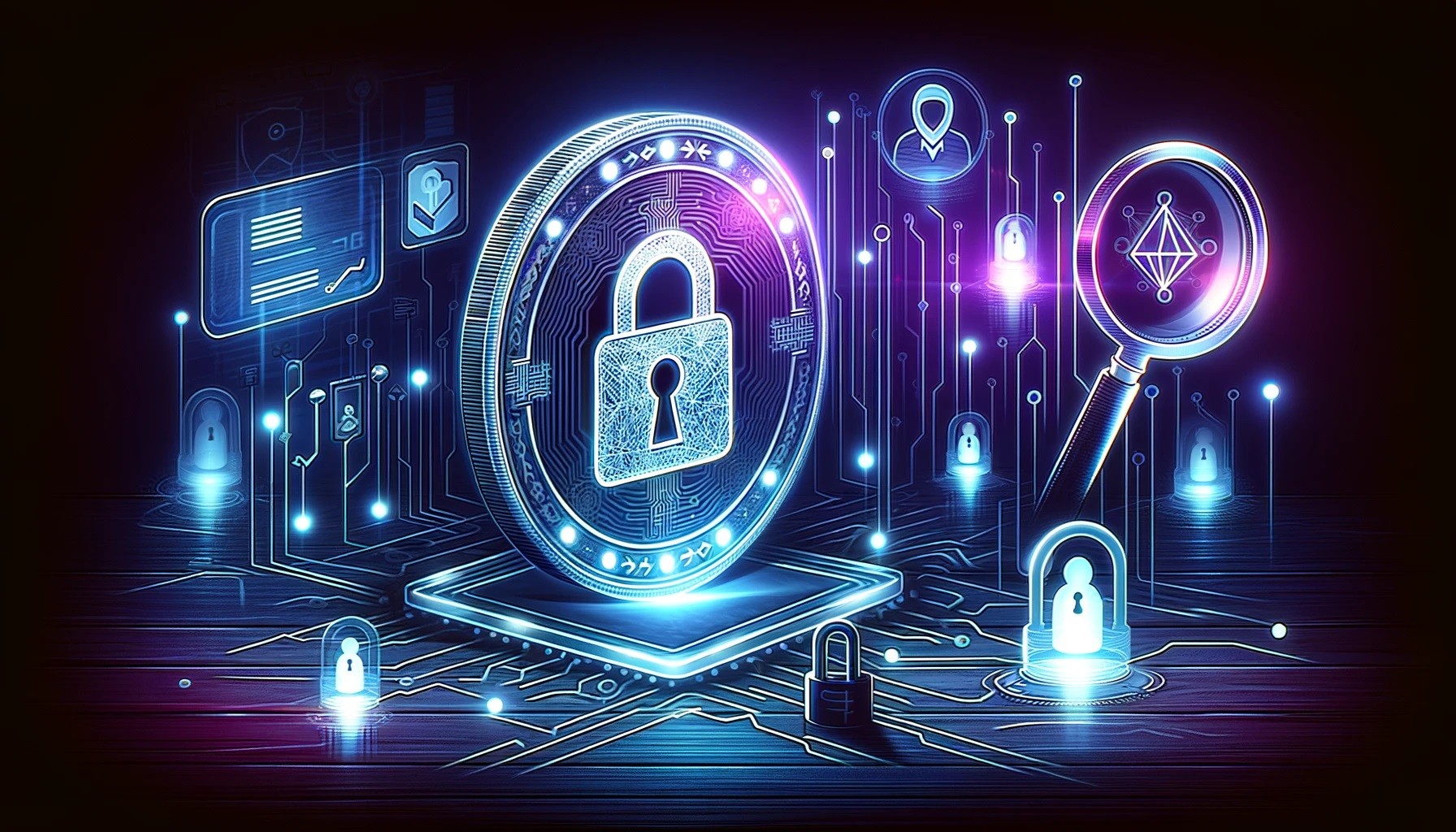
The process pattern of anonymity and pseudonymity. Source: ResearchGate
In digital assets, "anonymity" and "pseudonymity" are sometimes interchangeable. Therefore, traders who Google "Is Crypto anonymous?" may be slightly perplexed. Despite their similarities, it's vital to recognize the contrasts between these two ideas. Being completely unidentified or untraceable is referred to as anonymity. Any transaction or activity in a truly anonymous system cannot be connected to a particular person or organization.
Consider wearing a disguise that hides who you are, making it hard for anyone to identify you. In a nutshell, that is anonymity. If applied to crypto transactions, this would address the "is crypto anonymous" dilemma.
On the other hand, pseudonymity refers to a system in which people are identified by an alias or pseudonym instead of their true identity. It's similar to using a moniker on the internet. Even though your true identity is concealed, your activities and pseudonyms are still connected. Knowing the distinction between anonymity and pseudonymity is essential when discussing digital assets and privacy. It lets traders stop questioning whether Bitcoin is private and set reasonable expectations for each cryptocurrency's confidentiality.
The Myth of Anonymity in Cryptocurrency
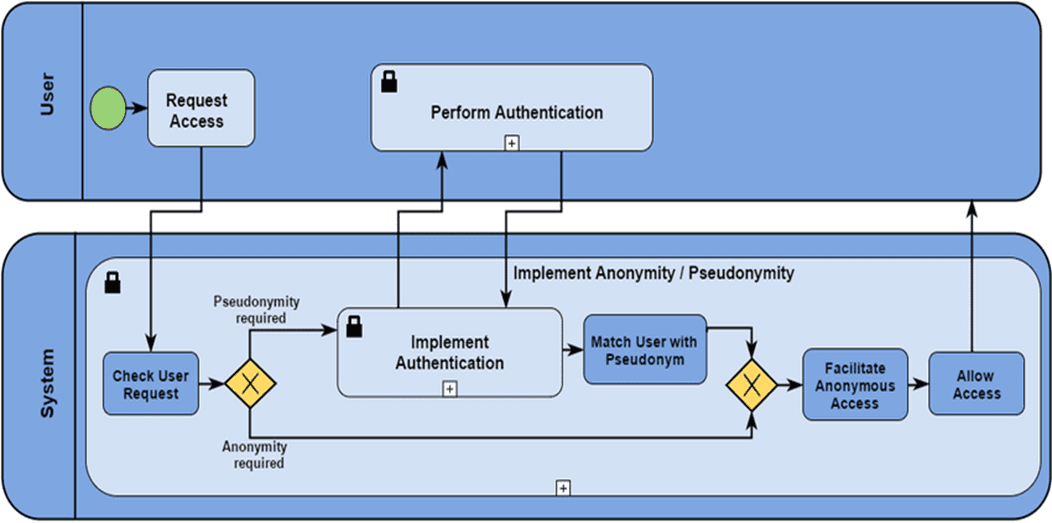
How BTC is being grouped. Source: Chainalysis
According to a report by Chainalysis, 60% of Bitcoin transaction volume is linked to entities that can be identified through exchanges. Blockchain.com data shows that over 450 million Bitcoin transactions have been recorded on the blockchain, all of which can be scrutinized for patterns.
Bitcoin and other popular cryptocurrencies are often believed to be entirely anonymous. This notion arises from early descriptions of crypto as "digital cash" that could be used with the same discretion as physical cash.
However, unlike physical cash, most cryptocurrencies operate on public ledgers that anyone can inspect. The transactions are linked to public addresses rather than real-world identities, leading many to believe in complete anonymity incorrectly.
This pseudonymity can be deceiving, where addresses are not tied to actual names but are still visible on the blockchain. When users make transactions, their public addresses and transaction history are permanently recorded on the blockchain.
Bitcoin, for instance, records all transactions in a public ledger that anyone can access, making it possible to trace addresses and monitor the flow of funds. Even though addresses don’t reveal personal details by default, any link between an address and an identity can expose all associated transactions.
How Privacy Can Be Compromised
Chainalysis, a blockchain analytics company, works with government agencies to track over $1 trillion of transactions annually. Over 90% of all Bitcoin transactions can be linked to real-world identities due to KYC requirements and IP address traces.
Despite the pseudonymous nature of crypto, there are several ways through which privacy can be compromised. Public visibility of blockchain transactions allows anyone to inspect the flow of funds, potentially revealing sensitive information.
Here are the significant ways privacy can be compromised in the crypto space:
Public Ledgers: Blockchain networks like Bitcoin maintain a transparent public ledger. This means every transaction is open for anyone to see. If a wallet address is ever linked to your real identity, all past and future transactions can be traced back to you.
IP Address Tracing: When using a cryptocurrency wallet, the service you interact with might record your IP address, creating a potential link to your identity. Blockchain analytics companies can correlate transaction patterns with known IP addresses to identify users.
Exchange KYC Requirements: Most cryptocurrency exchanges are required by law to implement Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols, meaning users must submit identification documents. Once you link your identity to an exchange account, your transactions lose any sense of anonymity.
Understanding these privacy pitfalls can help users take measures to safeguard their identities. Awareness of how exchanges use KYC data or blockchain visibility enables more cautious behavior.
Privacy Coins: Are They Anonymous?
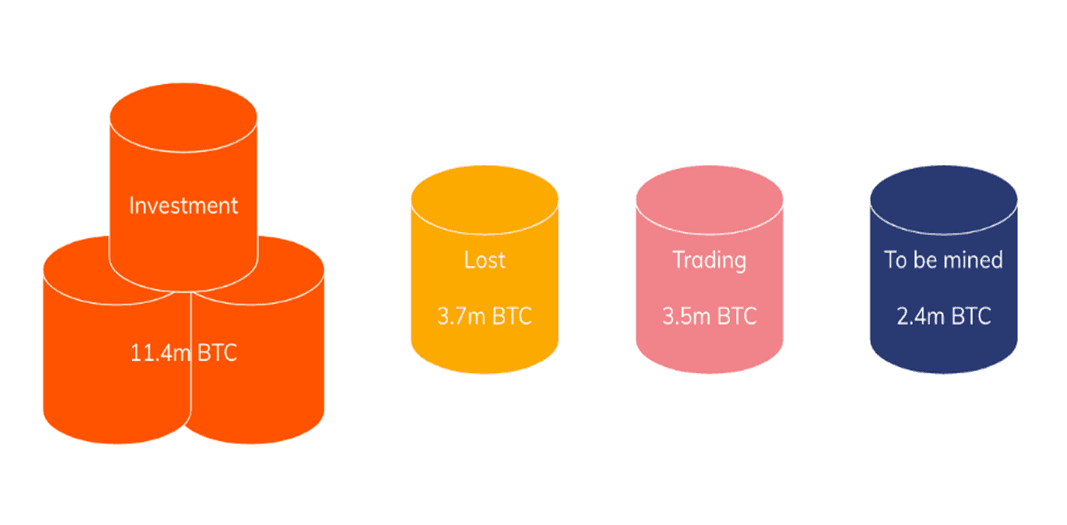
Examples of privacy coins, infrastructure, research, etc. Source: The Control via Medium
Privacy coins like Monero, Zcash, and Dash claim to offer enhanced privacy features. These coins are designed to address the privacy limitations inherent in Bitcoin and other mainstream cryptocurrencies.
While these coins provide advanced privacy measures, they are not without challenges. Understanding how each one works reveals whether they truly live up to the promise of anonymity.
Monero: Monero is one of the most well-known privacy coins. It uses advanced cryptographic techniques to obscure transaction details and the parties' identities. With features like ring signatures, stealth addresses, and confidential transactions, Monero enhances privacy by making transactions nearly impossible to trace.
Zcash: Zcash allows users to choose between transparent and shielded transactions. Shielded transactions use zk-SNARKs (zero-knowledge proofs) to keep transaction details confidential.
Limitations: Despite their privacy advantages, privacy coins face increased scrutiny from regulators. Governments are concerned that such coins could be used for illicit activities, leading to delistings from exchanges and restrictions on their use.
A report from CipherTrace showed that 42% of darknet market transactions involve privacy coins. Monero would be processed on the blockchain roughly 20,000 times daily in August 2024, a relatively stable figure indicating growing adoption. Privacy coins appeal to those seeking to hide their transactions, but users should consider the legal and regulatory landscape. As governments intensify efforts to combat money laundering and financial crimes, privacy coins are subject to restrictions.
The Role of Blockchain Analytics
Blockchain analytics firms, like Chainalysis and Elliptic, have become prominent due to their ability to de-anonymize transactions and track illicit activities.
How do these firms work? They analyze blockchain data to detect patterns, trace wallet addresses, and correlate transactions with known entities. Governments often use their services to track financial crimes, monitor suspicious activities, and recover stolen funds.
Tracking Mechanisms
Blockchain analytics firms use various methods to monitor and trace cryptocurrency transactions. These methods include clustering wallet addresses to identify related transactions, analysing transaction patterns to detect suspicious activities, and linking wallet addresses to IP addresses or known entities to pinpoint user identities. Advanced techniques like transaction graph analysis can also reveal connections between different addresses, enabling firms to uncover complex networks of transactions.
Forensic Capabilities
Authorities are relying on blockchain analytics for forensic investigations. They can find suspects and retrieve stolen money by tracking transactions linked to illicit operations such as drug trafficking, money laundering, ransomware payments, and cybercrime. The FBI's tracking of Bitcoin during the Silk Road investigation is one notable example of how analytics can be used to link illegal activity to actual people. Dismantling darknet markets, capturing cryptocurrency assets connected to criminal organizations, and monitoring money used to finance terrorism have all benefited greatly from these capabilities.
Understanding the capabilities of blockchain analytics highlights the importance of using privacy-preserving techniques when transacting with crypto. Users who value privacy must be aware of how transactions can be traced.
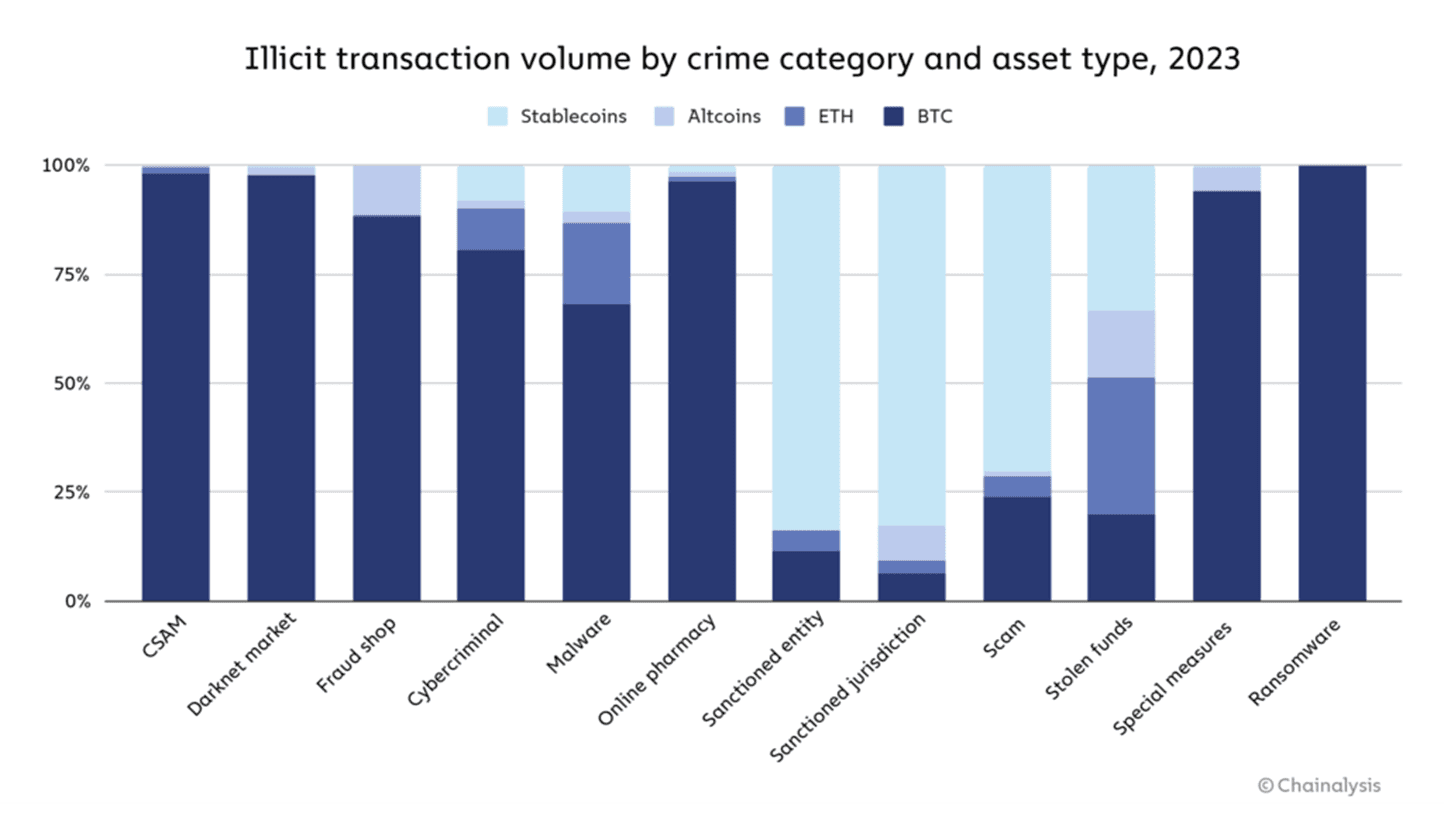
Illicit transaction volume by crime category and asset type in 2023. Source: Chainalysis
Blockchain analytics companies have helped recover over $10 billion in illicit funds in 2023 alone. The FBI reported that over 75% of cybercrime investigations now involve some form of blockchain analytics.
Best Practices for Protecting Your Privacy
For anonymity, over 40% of crypto users who care about privacy use VPNs or Tor. With a more than 50% market share, Monero remains the most popular privacy coin for darknet transactions.
There are methods to improve your privacy, even though cryptocurrency doesn't provide total anonymity. Implementing a few strategies can considerably decrease the probability of being monitored.
The following are some doable actions to safeguard your privacy:
Use Privacy Coins: Use coins like Monero or Zcash's shielded transactions for better privacy. They employ sophisticated cryptography, which makes tracking challenging.
Mixing Services: To hide the source of the money, cryptocurrency mixing services, also known as tumblers, combine several transactions. Users should exercise caution, though, as certain mixing services can be connected to illicit activity.
VPN and Tor: To conceal your IP address when conducting cryptocurrency transactions, use a VPN or the Tor network. These programs provide an extra layer of privacy and anonymize your internet connection.
Following these best practices can help users maintain a higher level of privacy while transacting with crypto, even in a world where surveillance is increasing.
Conclusion
While cryptocurrencies offer pseudonymity, they do not guarantee complete anonymity. Public blockchains, IP tracking, and KYC requirements compromise privacy. Privacy coins and best practices can help, but limitations and regulatory pressures exist.
The future of cryptocurrency may include better privacy features, such as advanced cryptographic techniques and more widespread use of privacy coins. Users must be mindful of the risks and limitations and adopt privacy-preserving strategies.
FAQs
Is cryptocurrency completely anonymous?
No, it's pseudonymous; transactions are linked to addresses, not personal identities, but can still be traced.
How can my privacy be compromised when using cryptocurrency?
Through public ledgers, IP address tracing, and KYC requirements linking identities to transactions.
Can my crypto be traced?
You can trace crypto wallets via public transaction records on the blockchain, though identifying the owner may require additional information.
Is crypto traceable to a person?
Yes, cryptocurrency transactions, including Bitcoin, can be traced. Each transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain is recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain.
Are privacy coins like Monero and Zcash genuinely anonymous?
Monero and Zcash enhance privacy but aren't anonymous due to regulatory pressures and usage restrictions.
Due to the misconception that cryptocurrency guarantees total privacy, many users believe they may make transactions without leaving any identity record.
Because blockchain technology is complex and sometimes misinterpreted, the myth that cryptocurrencies provide total anonymity endures. Although specific features offer a degree of privacy, anonymity falls in some aspects.
This post will reveal the truth about blockchain privacy by analyzing the distinctions between anonymity and pseudonymity, how privacy might be jeopardized, the role of privacy coins, crypto traceable transactions, blockchain analytics, and best practices for safeguarding your privacy. We’ll explain what happens behind the scenes of crypto transactions and provide practical ways to enhance privacy.
Anonymity vs Pseudonymity

The process pattern of anonymity and pseudonymity. Source: ResearchGate
In digital assets, "anonymity" and "pseudonymity" are sometimes interchangeable. Therefore, traders who Google "Is Crypto anonymous?" may be slightly perplexed. Despite their similarities, it's vital to recognize the contrasts between these two ideas. Being completely unidentified or untraceable is referred to as anonymity. Any transaction or activity in a truly anonymous system cannot be connected to a particular person or organization.
Consider wearing a disguise that hides who you are, making it hard for anyone to identify you. In a nutshell, that is anonymity. If applied to crypto transactions, this would address the "is crypto anonymous" dilemma.
On the other hand, pseudonymity refers to a system in which people are identified by an alias or pseudonym instead of their true identity. It's similar to using a moniker on the internet. Even though your true identity is concealed, your activities and pseudonyms are still connected. Knowing the distinction between anonymity and pseudonymity is essential when discussing digital assets and privacy. It lets traders stop questioning whether Bitcoin is private and set reasonable expectations for each cryptocurrency's confidentiality.
The Myth of Anonymity in Cryptocurrency

How BTC is being grouped. Source: Chainalysis
According to a report by Chainalysis, 60% of Bitcoin transaction volume is linked to entities that can be identified through exchanges. Blockchain.com data shows that over 450 million Bitcoin transactions have been recorded on the blockchain, all of which can be scrutinized for patterns.
Bitcoin and other popular cryptocurrencies are often believed to be entirely anonymous. This notion arises from early descriptions of crypto as "digital cash" that could be used with the same discretion as physical cash.
However, unlike physical cash, most cryptocurrencies operate on public ledgers that anyone can inspect. The transactions are linked to public addresses rather than real-world identities, leading many to believe in complete anonymity incorrectly.
This pseudonymity can be deceiving, where addresses are not tied to actual names but are still visible on the blockchain. When users make transactions, their public addresses and transaction history are permanently recorded on the blockchain.
Bitcoin, for instance, records all transactions in a public ledger that anyone can access, making it possible to trace addresses and monitor the flow of funds. Even though addresses don’t reveal personal details by default, any link between an address and an identity can expose all associated transactions.
How Privacy Can Be Compromised
Chainalysis, a blockchain analytics company, works with government agencies to track over $1 trillion of transactions annually. Over 90% of all Bitcoin transactions can be linked to real-world identities due to KYC requirements and IP address traces.
Despite the pseudonymous nature of crypto, there are several ways through which privacy can be compromised. Public visibility of blockchain transactions allows anyone to inspect the flow of funds, potentially revealing sensitive information.
Here are the significant ways privacy can be compromised in the crypto space:
Public Ledgers: Blockchain networks like Bitcoin maintain a transparent public ledger. This means every transaction is open for anyone to see. If a wallet address is ever linked to your real identity, all past and future transactions can be traced back to you.
IP Address Tracing: When using a cryptocurrency wallet, the service you interact with might record your IP address, creating a potential link to your identity. Blockchain analytics companies can correlate transaction patterns with known IP addresses to identify users.
Exchange KYC Requirements: Most cryptocurrency exchanges are required by law to implement Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols, meaning users must submit identification documents. Once you link your identity to an exchange account, your transactions lose any sense of anonymity.
Understanding these privacy pitfalls can help users take measures to safeguard their identities. Awareness of how exchanges use KYC data or blockchain visibility enables more cautious behavior.
Privacy Coins: Are They Anonymous?

Examples of privacy coins, infrastructure, research, etc. Source: The Control via Medium
Privacy coins like Monero, Zcash, and Dash claim to offer enhanced privacy features. These coins are designed to address the privacy limitations inherent in Bitcoin and other mainstream cryptocurrencies.
While these coins provide advanced privacy measures, they are not without challenges. Understanding how each one works reveals whether they truly live up to the promise of anonymity.
Monero: Monero is one of the most well-known privacy coins. It uses advanced cryptographic techniques to obscure transaction details and the parties' identities. With features like ring signatures, stealth addresses, and confidential transactions, Monero enhances privacy by making transactions nearly impossible to trace.
Zcash: Zcash allows users to choose between transparent and shielded transactions. Shielded transactions use zk-SNARKs (zero-knowledge proofs) to keep transaction details confidential.
Limitations: Despite their privacy advantages, privacy coins face increased scrutiny from regulators. Governments are concerned that such coins could be used for illicit activities, leading to delistings from exchanges and restrictions on their use.
A report from CipherTrace showed that 42% of darknet market transactions involve privacy coins. Monero would be processed on the blockchain roughly 20,000 times daily in August 2024, a relatively stable figure indicating growing adoption. Privacy coins appeal to those seeking to hide their transactions, but users should consider the legal and regulatory landscape. As governments intensify efforts to combat money laundering and financial crimes, privacy coins are subject to restrictions.
The Role of Blockchain Analytics
Blockchain analytics firms, like Chainalysis and Elliptic, have become prominent due to their ability to de-anonymize transactions and track illicit activities.
How do these firms work? They analyze blockchain data to detect patterns, trace wallet addresses, and correlate transactions with known entities. Governments often use their services to track financial crimes, monitor suspicious activities, and recover stolen funds.
Tracking Mechanisms
Blockchain analytics firms use various methods to monitor and trace cryptocurrency transactions. These methods include clustering wallet addresses to identify related transactions, analysing transaction patterns to detect suspicious activities, and linking wallet addresses to IP addresses or known entities to pinpoint user identities. Advanced techniques like transaction graph analysis can also reveal connections between different addresses, enabling firms to uncover complex networks of transactions.
Forensic Capabilities
Authorities are relying on blockchain analytics for forensic investigations. They can find suspects and retrieve stolen money by tracking transactions linked to illicit operations such as drug trafficking, money laundering, ransomware payments, and cybercrime. The FBI's tracking of Bitcoin during the Silk Road investigation is one notable example of how analytics can be used to link illegal activity to actual people. Dismantling darknet markets, capturing cryptocurrency assets connected to criminal organizations, and monitoring money used to finance terrorism have all benefited greatly from these capabilities.
Understanding the capabilities of blockchain analytics highlights the importance of using privacy-preserving techniques when transacting with crypto. Users who value privacy must be aware of how transactions can be traced.

Illicit transaction volume by crime category and asset type in 2023. Source: Chainalysis
Blockchain analytics companies have helped recover over $10 billion in illicit funds in 2023 alone. The FBI reported that over 75% of cybercrime investigations now involve some form of blockchain analytics.
Best Practices for Protecting Your Privacy
For anonymity, over 40% of crypto users who care about privacy use VPNs or Tor. With a more than 50% market share, Monero remains the most popular privacy coin for darknet transactions.
There are methods to improve your privacy, even though cryptocurrency doesn't provide total anonymity. Implementing a few strategies can considerably decrease the probability of being monitored.
The following are some doable actions to safeguard your privacy:
Use Privacy Coins: Use coins like Monero or Zcash's shielded transactions for better privacy. They employ sophisticated cryptography, which makes tracking challenging.
Mixing Services: To hide the source of the money, cryptocurrency mixing services, also known as tumblers, combine several transactions. Users should exercise caution, though, as certain mixing services can be connected to illicit activity.
VPN and Tor: To conceal your IP address when conducting cryptocurrency transactions, use a VPN or the Tor network. These programs provide an extra layer of privacy and anonymize your internet connection.
Following these best practices can help users maintain a higher level of privacy while transacting with crypto, even in a world where surveillance is increasing.
Conclusion
While cryptocurrencies offer pseudonymity, they do not guarantee complete anonymity. Public blockchains, IP tracking, and KYC requirements compromise privacy. Privacy coins and best practices can help, but limitations and regulatory pressures exist.
The future of cryptocurrency may include better privacy features, such as advanced cryptographic techniques and more widespread use of privacy coins. Users must be mindful of the risks and limitations and adopt privacy-preserving strategies.
FAQs
Is cryptocurrency completely anonymous?
No, it's pseudonymous; transactions are linked to addresses, not personal identities, but can still be traced.
How can my privacy be compromised when using cryptocurrency?
Through public ledgers, IP address tracing, and KYC requirements linking identities to transactions.
Can my crypto be traced?
You can trace crypto wallets via public transaction records on the blockchain, though identifying the owner may require additional information.
Is crypto traceable to a person?
Yes, cryptocurrency transactions, including Bitcoin, can be traced. Each transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain is recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain.
Are privacy coins like Monero and Zcash genuinely anonymous?
Monero and Zcash enhance privacy but aren't anonymous due to regulatory pressures and usage restrictions.
Due to the misconception that cryptocurrency guarantees total privacy, many users believe they may make transactions without leaving any identity record.
Because blockchain technology is complex and sometimes misinterpreted, the myth that cryptocurrencies provide total anonymity endures. Although specific features offer a degree of privacy, anonymity falls in some aspects.
This post will reveal the truth about blockchain privacy by analyzing the distinctions between anonymity and pseudonymity, how privacy might be jeopardized, the role of privacy coins, crypto traceable transactions, blockchain analytics, and best practices for safeguarding your privacy. We’ll explain what happens behind the scenes of crypto transactions and provide practical ways to enhance privacy.
Anonymity vs Pseudonymity

The process pattern of anonymity and pseudonymity. Source: ResearchGate
In digital assets, "anonymity" and "pseudonymity" are sometimes interchangeable. Therefore, traders who Google "Is Crypto anonymous?" may be slightly perplexed. Despite their similarities, it's vital to recognize the contrasts between these two ideas. Being completely unidentified or untraceable is referred to as anonymity. Any transaction or activity in a truly anonymous system cannot be connected to a particular person or organization.
Consider wearing a disguise that hides who you are, making it hard for anyone to identify you. In a nutshell, that is anonymity. If applied to crypto transactions, this would address the "is crypto anonymous" dilemma.
On the other hand, pseudonymity refers to a system in which people are identified by an alias or pseudonym instead of their true identity. It's similar to using a moniker on the internet. Even though your true identity is concealed, your activities and pseudonyms are still connected. Knowing the distinction between anonymity and pseudonymity is essential when discussing digital assets and privacy. It lets traders stop questioning whether Bitcoin is private and set reasonable expectations for each cryptocurrency's confidentiality.
The Myth of Anonymity in Cryptocurrency

How BTC is being grouped. Source: Chainalysis
According to a report by Chainalysis, 60% of Bitcoin transaction volume is linked to entities that can be identified through exchanges. Blockchain.com data shows that over 450 million Bitcoin transactions have been recorded on the blockchain, all of which can be scrutinized for patterns.
Bitcoin and other popular cryptocurrencies are often believed to be entirely anonymous. This notion arises from early descriptions of crypto as "digital cash" that could be used with the same discretion as physical cash.
However, unlike physical cash, most cryptocurrencies operate on public ledgers that anyone can inspect. The transactions are linked to public addresses rather than real-world identities, leading many to believe in complete anonymity incorrectly.
This pseudonymity can be deceiving, where addresses are not tied to actual names but are still visible on the blockchain. When users make transactions, their public addresses and transaction history are permanently recorded on the blockchain.
Bitcoin, for instance, records all transactions in a public ledger that anyone can access, making it possible to trace addresses and monitor the flow of funds. Even though addresses don’t reveal personal details by default, any link between an address and an identity can expose all associated transactions.
How Privacy Can Be Compromised
Chainalysis, a blockchain analytics company, works with government agencies to track over $1 trillion of transactions annually. Over 90% of all Bitcoin transactions can be linked to real-world identities due to KYC requirements and IP address traces.
Despite the pseudonymous nature of crypto, there are several ways through which privacy can be compromised. Public visibility of blockchain transactions allows anyone to inspect the flow of funds, potentially revealing sensitive information.
Here are the significant ways privacy can be compromised in the crypto space:
Public Ledgers: Blockchain networks like Bitcoin maintain a transparent public ledger. This means every transaction is open for anyone to see. If a wallet address is ever linked to your real identity, all past and future transactions can be traced back to you.
IP Address Tracing: When using a cryptocurrency wallet, the service you interact with might record your IP address, creating a potential link to your identity. Blockchain analytics companies can correlate transaction patterns with known IP addresses to identify users.
Exchange KYC Requirements: Most cryptocurrency exchanges are required by law to implement Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols, meaning users must submit identification documents. Once you link your identity to an exchange account, your transactions lose any sense of anonymity.
Understanding these privacy pitfalls can help users take measures to safeguard their identities. Awareness of how exchanges use KYC data or blockchain visibility enables more cautious behavior.
Privacy Coins: Are They Anonymous?

Examples of privacy coins, infrastructure, research, etc. Source: The Control via Medium
Privacy coins like Monero, Zcash, and Dash claim to offer enhanced privacy features. These coins are designed to address the privacy limitations inherent in Bitcoin and other mainstream cryptocurrencies.
While these coins provide advanced privacy measures, they are not without challenges. Understanding how each one works reveals whether they truly live up to the promise of anonymity.
Monero: Monero is one of the most well-known privacy coins. It uses advanced cryptographic techniques to obscure transaction details and the parties' identities. With features like ring signatures, stealth addresses, and confidential transactions, Monero enhances privacy by making transactions nearly impossible to trace.
Zcash: Zcash allows users to choose between transparent and shielded transactions. Shielded transactions use zk-SNARKs (zero-knowledge proofs) to keep transaction details confidential.
Limitations: Despite their privacy advantages, privacy coins face increased scrutiny from regulators. Governments are concerned that such coins could be used for illicit activities, leading to delistings from exchanges and restrictions on their use.
A report from CipherTrace showed that 42% of darknet market transactions involve privacy coins. Monero would be processed on the blockchain roughly 20,000 times daily in August 2024, a relatively stable figure indicating growing adoption. Privacy coins appeal to those seeking to hide their transactions, but users should consider the legal and regulatory landscape. As governments intensify efforts to combat money laundering and financial crimes, privacy coins are subject to restrictions.
The Role of Blockchain Analytics
Blockchain analytics firms, like Chainalysis and Elliptic, have become prominent due to their ability to de-anonymize transactions and track illicit activities.
How do these firms work? They analyze blockchain data to detect patterns, trace wallet addresses, and correlate transactions with known entities. Governments often use their services to track financial crimes, monitor suspicious activities, and recover stolen funds.
Tracking Mechanisms
Blockchain analytics firms use various methods to monitor and trace cryptocurrency transactions. These methods include clustering wallet addresses to identify related transactions, analysing transaction patterns to detect suspicious activities, and linking wallet addresses to IP addresses or known entities to pinpoint user identities. Advanced techniques like transaction graph analysis can also reveal connections between different addresses, enabling firms to uncover complex networks of transactions.
Forensic Capabilities
Authorities are relying on blockchain analytics for forensic investigations. They can find suspects and retrieve stolen money by tracking transactions linked to illicit operations such as drug trafficking, money laundering, ransomware payments, and cybercrime. The FBI's tracking of Bitcoin during the Silk Road investigation is one notable example of how analytics can be used to link illegal activity to actual people. Dismantling darknet markets, capturing cryptocurrency assets connected to criminal organizations, and monitoring money used to finance terrorism have all benefited greatly from these capabilities.
Understanding the capabilities of blockchain analytics highlights the importance of using privacy-preserving techniques when transacting with crypto. Users who value privacy must be aware of how transactions can be traced.

Illicit transaction volume by crime category and asset type in 2023. Source: Chainalysis
Blockchain analytics companies have helped recover over $10 billion in illicit funds in 2023 alone. The FBI reported that over 75% of cybercrime investigations now involve some form of blockchain analytics.
Best Practices for Protecting Your Privacy
For anonymity, over 40% of crypto users who care about privacy use VPNs or Tor. With a more than 50% market share, Monero remains the most popular privacy coin for darknet transactions.
There are methods to improve your privacy, even though cryptocurrency doesn't provide total anonymity. Implementing a few strategies can considerably decrease the probability of being monitored.
The following are some doable actions to safeguard your privacy:
Use Privacy Coins: Use coins like Monero or Zcash's shielded transactions for better privacy. They employ sophisticated cryptography, which makes tracking challenging.
Mixing Services: To hide the source of the money, cryptocurrency mixing services, also known as tumblers, combine several transactions. Users should exercise caution, though, as certain mixing services can be connected to illicit activity.
VPN and Tor: To conceal your IP address when conducting cryptocurrency transactions, use a VPN or the Tor network. These programs provide an extra layer of privacy and anonymize your internet connection.
Following these best practices can help users maintain a higher level of privacy while transacting with crypto, even in a world where surveillance is increasing.
Conclusion
While cryptocurrencies offer pseudonymity, they do not guarantee complete anonymity. Public blockchains, IP tracking, and KYC requirements compromise privacy. Privacy coins and best practices can help, but limitations and regulatory pressures exist.
The future of cryptocurrency may include better privacy features, such as advanced cryptographic techniques and more widespread use of privacy coins. Users must be mindful of the risks and limitations and adopt privacy-preserving strategies.
FAQs
Is cryptocurrency completely anonymous?
No, it's pseudonymous; transactions are linked to addresses, not personal identities, but can still be traced.
How can my privacy be compromised when using cryptocurrency?
Through public ledgers, IP address tracing, and KYC requirements linking identities to transactions.
Can my crypto be traced?
You can trace crypto wallets via public transaction records on the blockchain, though identifying the owner may require additional information.
Is crypto traceable to a person?
Yes, cryptocurrency transactions, including Bitcoin, can be traced. Each transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain is recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain.
Are privacy coins like Monero and Zcash genuinely anonymous?
Monero and Zcash enhance privacy but aren't anonymous due to regulatory pressures and usage restrictions.
Future of Crypto is Here
Join for early bird access, perks and more!
Future of Crypto is Here
Join for early bird access, perks and more!
Future of Crypto is Here
Join for early bird access, perks and more!
Future of Crypto is Here
Join for early bird access, perks and more!
Future of Crypto is Here
Join for early bird access, perks and more!
Future of Crypto is Here
Join for early bird access, perks and more!